Community-Based Rehabilitation (CBR) is a community development strategy designed to improve the quality of life for persons with disabilities and their families. It promotes the inclusion, participation, and empowerment of persons with disabilities within their communities by addressing both physical and sociological barriers to participation.
Originally launched by the World Health Organization (WHO) to expand access to rehabilitation services at the community level, CBR has evolved into a comprehensive, multisectoral approach that is now recognized as a core strategy for community-based inclusive development (CBID).
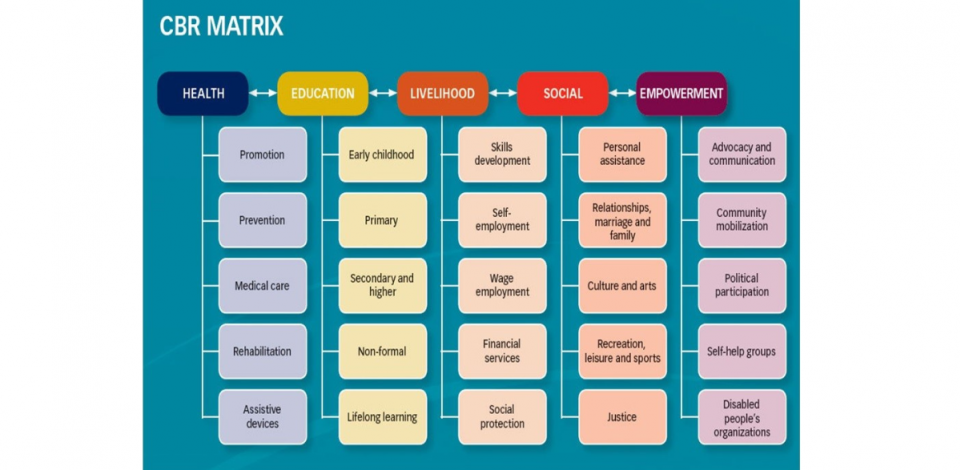
CBR addresses five interconnected components:
- Health
- Education
- Livelihood
- Social inclusion
- Empowerment
These components can be adapted based on context-specific needs and context. They are not meant to be implemented sequentially, but rather as a flexible framework – similar to a “pick-and-mix” model that enables customized, context-specific interventions.
CBR is carried out through the collaborative efforts of:
- Persons with disabilities
- Families and community members
- Government and non-government stakeholders across health, education, vocational, and social sectors
By linking community resources with existing government services, CBR supports disability-inclusive development and addresses both rehabilitation needs and social exclusion, especially for those affected by Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs).
For which NTDs is this relevant?
CBR is particularly relevant for NTDs that lead to disability or social exclusion. The strategies used in CBR are broadly applicable across NTDs. Rather than creating parallel programs, people with NTD-related disabilities should be integrated into general CBR initiatives. These programs should offer inclusive services, although access to specialized care (e.g., hydrocele surgery, braille materials) depends on context-specific availability.
An example of CBR in practice is the work of the Christian Blind Mission (CBM), an organization committed to improving the quality of life of people with disabilities. CBM actively supports CBR and eye health activities within the NTD control programs for the five major NTDs, including trachoma, onchocerciasis, lymphatic filariasis, schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminths, demonstrating how CBR can be effectively integrated into public health and development efforts.
